Robust AI Planning
Keywords:
Autonomous systems, AI PlanningAbstract
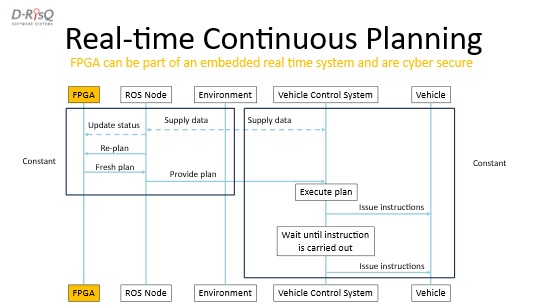
Autonomous systems are intended to be used to achieve tasks that enable humans to be removed from dull, dirty, or dangerous situations. In order to be able to do this autonomously, there are 2 main constraints: Reliability and Safety. An element of reliability is persistence, in other words, the ability to continue to achieve a task safely, and is the focus of this paper. In order to do this without human intervention, there has to be an ability to provide the system with a plan of how to achieve a task. AI Planning is a computer science discipline that has been used in various scenarios where some degree of autonomy is required for the computer system. Its use relies upon inputs that describe a task that needs to be achieved, a language that can be used to describe the task, and a machine called a “solver”. The output is typically a plan that may be used to try to achieve the task. The types of tasks can range from route planning to cyber-attack, and the output is a plan in the form of a program to be followed. However, there are a number of issues with the usual approaches. AI planning tools typically require the use of elastic resources, memory and processing power, so use of the cloud helps with the computational effort and hence is an off-line activity. Further, the use of heuristics means that AI planning tools might not even return an answer. Replanning when conditions change in the environment or in the system therefore presents issues for embedded real-time systems. This paper will outline the issues with typical approaches, and present a potential solution for generating domain-specific planners implemented on hardware. The dedicated planner enables real-time replanning and the whole approach is placed in conjunction with safety assurance.
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 D-RisQ Ltd.You may use this work providing you clearly acknowledge the Author (or their copyright holder) and the Safety-Critical Systems eJournal.

